Creating Resilience
Workplace & Occupancy Management Technology in 2024
The Technology Solutions Driving Workplace Efficiency and Effectiveness
April 29, 2024 8 Minute Read

Executive Summary
Best Practices for Major Office Occupiers
Read MoreThis report focuses on global workplace technology data derived from CBRE clients representing 350 million sq. ft./32 million sq. m. and provides insights by portfolio size and geography. Building on the technological trends identified in CBRE’s 2023-2024 Global Workplace & Occupancy Insights Report, this analysis will help CRE leaders craft a workplace technology strategy that aligns seamlessly with business requirements and culture objectives.
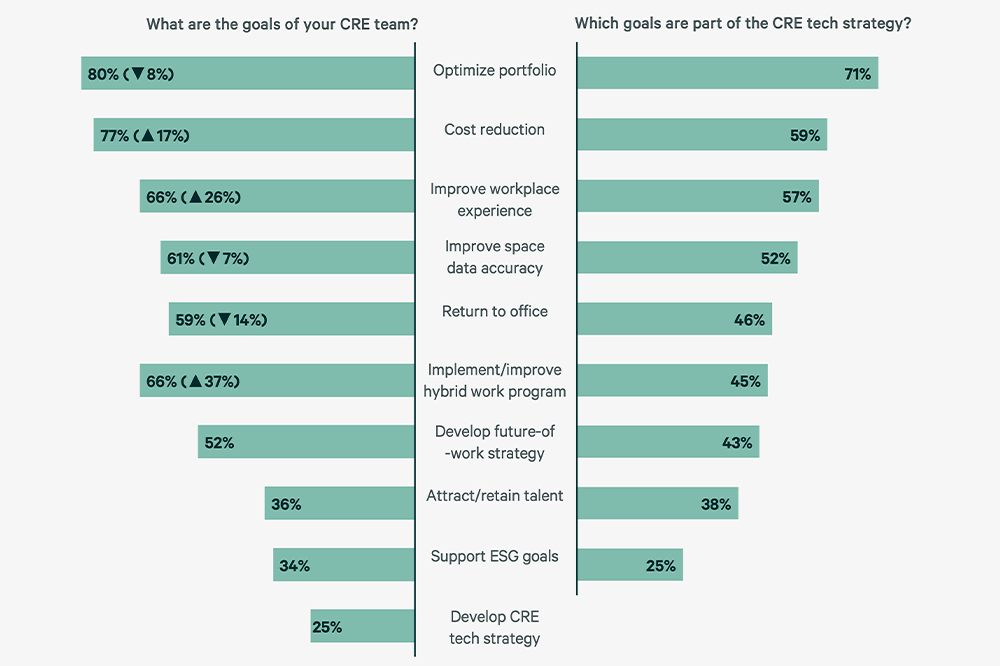
Organizations are placing a greater emphasis on how real estate supports workplace effectiveness rather than relying on traditional metrics such as square feet or square meters per person. Notably, there has been a substantial 37% increase in goals dedicated to enhancing the workplace experience.
In tandem, the evolution of occupancy metrics is reshaping how organizations measure success. The shift from traditional density metrics to performance indicators, such as employee sentiment and attendance, reflects a fundamental change in measuring workplace efficacy.
Central to this transformation is better data, investment in new and evolving workplace technology and development of a cohesive technology toolkit. This often includes the integration of space management systems, utilization analysis tools and employee experience applications that aggregate data. Best practices begin with a diagnostic assessment, documenting a technology roadmap, and establishing a data governance program. These measures are critical for informed decision-making to build an attractive workplace.

Technology Strategy
To understand the impact the physical and virtual work experience has on business goals, we must move past simply tracking workplace efficiencies and measure workplace effectiveness.
Measuring Workplace Efficiency and Effectiveness
Portfolio optimization and cost reduction have remained top objectives for participants in CBRE’s Global Workplace & Occupancy Insights surveys from 2021 to 2023. However, in 2023 there was a massive shift to measure and improve the workplace experience. CRE leaders once focused on portfolio cost efficiency are now being challenged to also make their spaces more effective. As a result, workplace leaders are prioritizing experience within their technology strategy.
Figure 1: CRE Team and Tech Strategy Goals
The New Occupancy Metrics That Matter Most
A growing number of participants are prioritizing metrics that measure how space performs over how space is planned. For example, space planning density metrics like sq. ft./sq. m. per person and sq. ft./sq. m. per seat have been replaced with workplace performance metrics such as employee sentiment, attendance or show-up rate.
Figure 2: Occupancy Metrics That Matter Most, 2021-2023
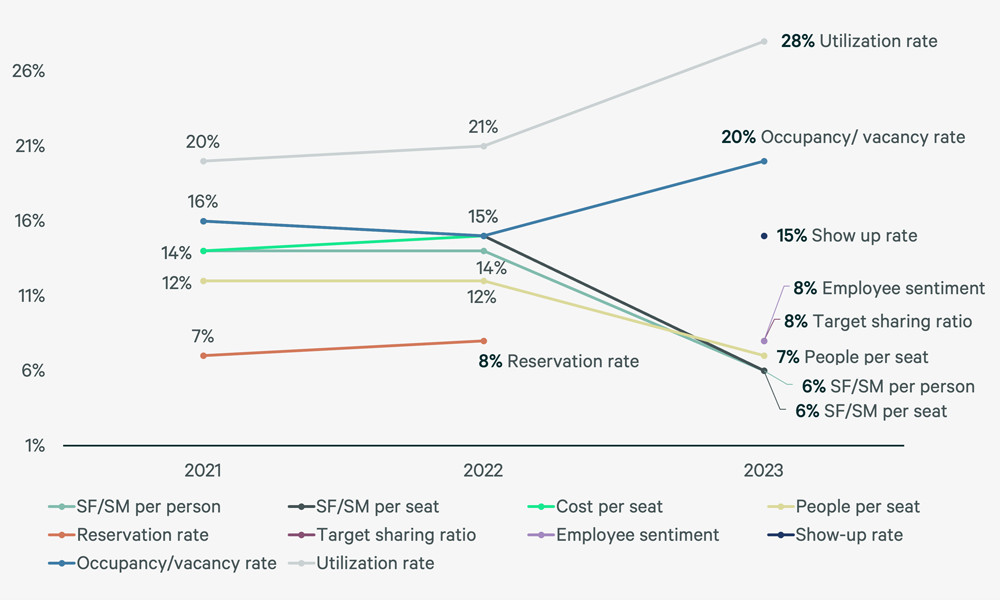
For the first time, sq. ft./sq. m. per person and sq. ft./sq. m. per seat are no longer in the top five metrics that matter most.
Supporting the Physical and Virtual Workplace Experience
To support the new focus on hybrid workplace experience, participants have expanded their traditional toolkit to include solutions that support both the physical and virtual work environments. This includes not only tools like employee experience apps and space reservation systems, but tools that leverage data from highly adopted communication and scheduling tools such as email, chat and calendars, which provide a rich source of existing data to inform workplace and hybrid workplace effectiveness.
Over 80% of participants integrate their workplace technology tools, either directly using application program interfaces (APIs) or indirectly through a data warehouse or lake, to create a connected eco-system that eliminates manual data entry, simplifies workflows and expands access to standardized data. The result is a scalable technology toolkit that improves employee experience, speeds decision making, and manages the workplace experience across physical and virtual environments.
Figure 3: Consolidated Workplace Technology Stack
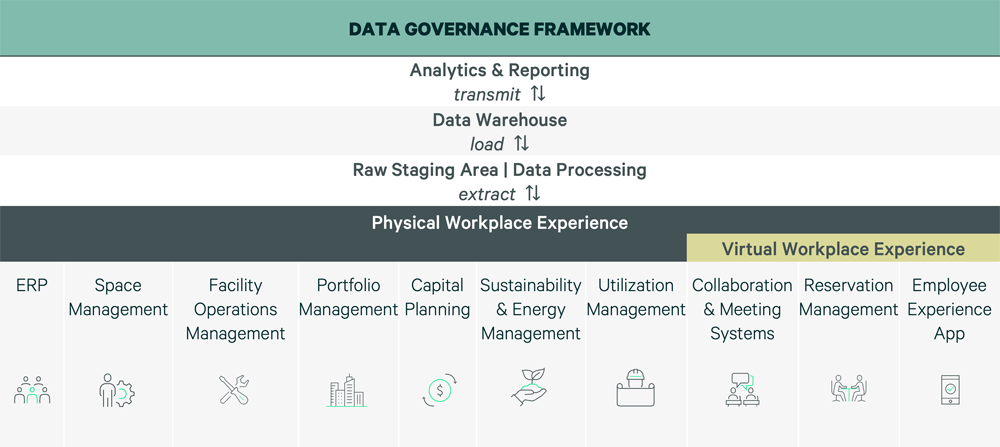
Technology Toolkit
The right workplace technology solutions depend on your unique portfolio dynamics, business priorities and cultural goals. Your organization’s technology maturity, a concept explored on the following pages (see Fig. 8), will determine the feasibility and value of incorporating workplace innovations such as digital twins, sensor-based dynamic planning, and AI-enabled analytics into your toolkit. Before exploring these innovations, it is critical to consider the following core tools that are fundamental to any workplace technology toolkit.
Digital twin: An exact digital replica of a physical building or space
Sensor-based dynamic planning: Ability to leverage occupancy sensor data to make informed decisions about space allocations and use
AI-enabled analytics: Analytics that provide organizations insights into employee behavior, space preferences and trends

Space Management Systems
Integrated Solutions Preferred
Over 80% of participants have automated integrations that push or pull data from their space management system. These integrations expedite the flow of work and improve data quality by providing a single source of truth for information.
Pro Tip: When evaluating the advantages of a space management strategy, assess the impact on your organization, including the value of flexibility, usability and user experience. Additionally, consider how the strategy aligns with and complements existing systems, maximizing the potential for leveraging implemented solutions.
Figure 4: How Data Is Integrated Across Technologies
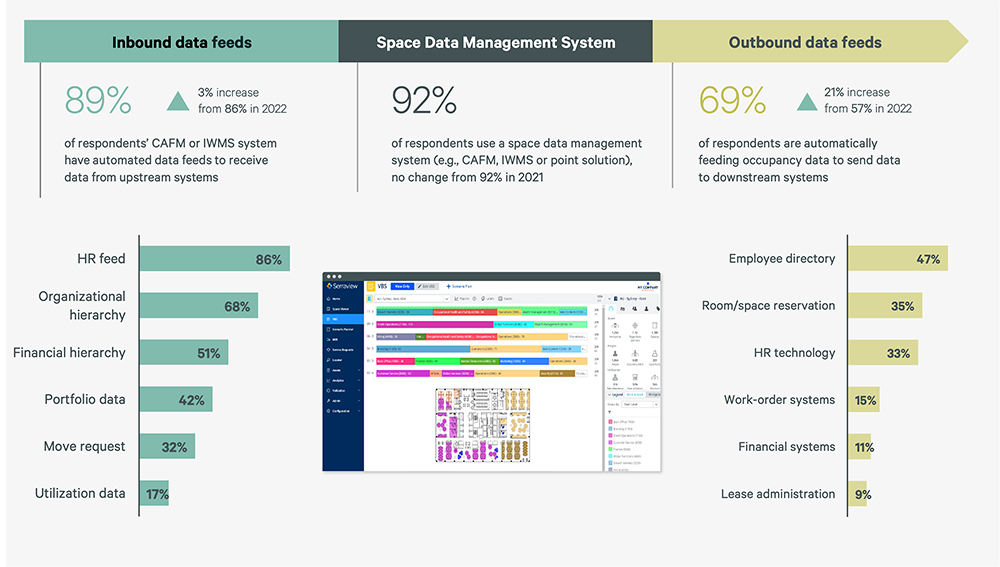
Space Utilization Management
An Untapped Resource for Smart Building Management
From Q2 2022 to Q2 2023 global average office utilization was 35%—a 45% decrease from the pre-pandemic global average of 64%. The operational and financial impacts of underutilized space is a top concern for CRE leaders, prompting many organizations to implement or expand utilization management solutions. Today, most participants rely on utilization data for portfolio strategy and demand planning, but we can expect the data to become increasingly important for smart building management as ESG goals are prioritized.
Occupancy: available space that is or can be occupied by people or equipment.
Utilization: how available space is being used over time.
Figure 5: How Is Utilization Data Used?
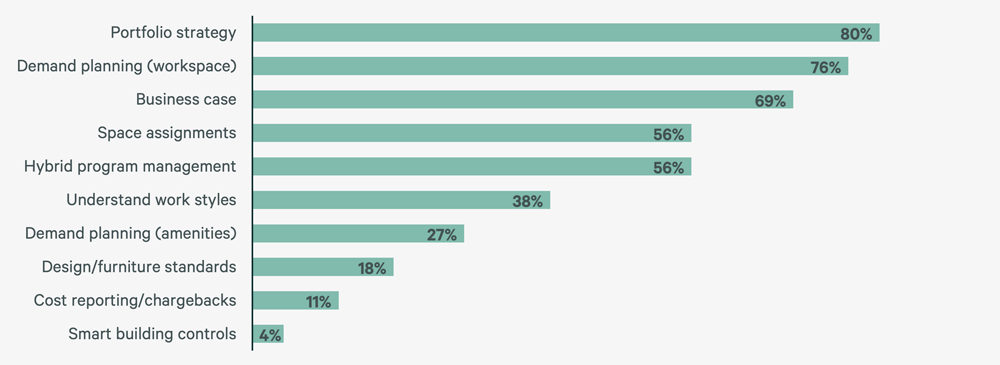
Macro Utilization Data Satisfied Clients in the Past but Micro Level Data is Needed for the Future
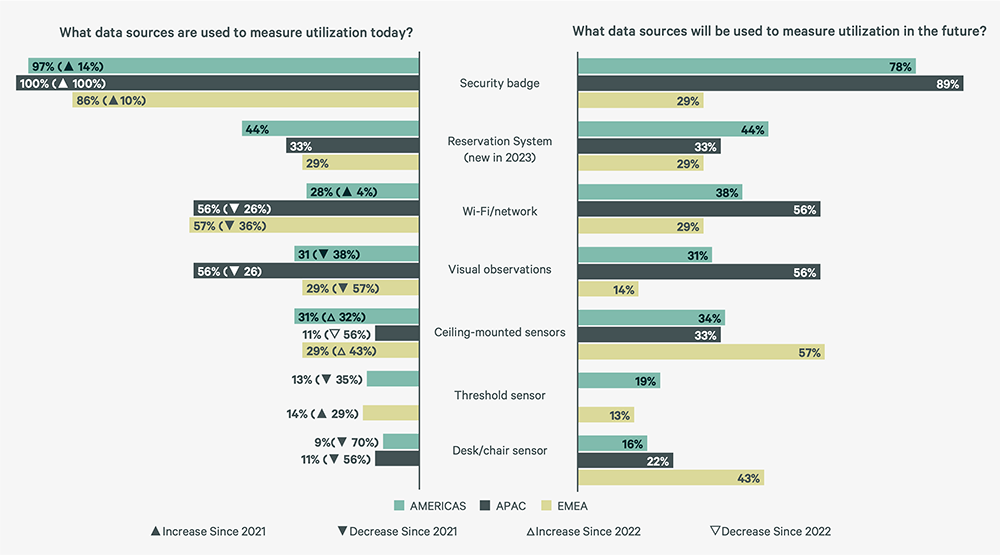
Of the 81% of participants who measure space utilization, 96% use badge swipe data, a 21% increase since 2021, driven by availability and relative costs to capture. Decreased use of Wi-Fi/network data (down 19% since 2021) and threshold and desk/chair sensors (down 42% and 68% respectively since 2021) suggests badge data has been sufficient to support macro portfolio objectives for many organizations.
Participants plan to enhance their utilization of Wi-Fi/network and sensor data in the future to accomplish a secondary set of objectives. This highlights a growing demand for more refined and superior quality micro data, essential for a diverse range of strategic analyses. Companies are now inclined to track not just the presence of individuals in a building or on a specific floor, as indicated by badge swipe data, but also the actual utilization and manner of space use. Wi-Fi/network data provides the information on presence within a space, while sensor data clarifies the specific activities and usage patterns within that space.
Understanding how employees engage with their surroundings helps organizations create more efficient and effective work environments that elevate the overall employee experience. These have the potential to inspire a return to the office, foster heightened morale and boost overall productivity.
Figure 6: Sources of Current & Future Utilization Data
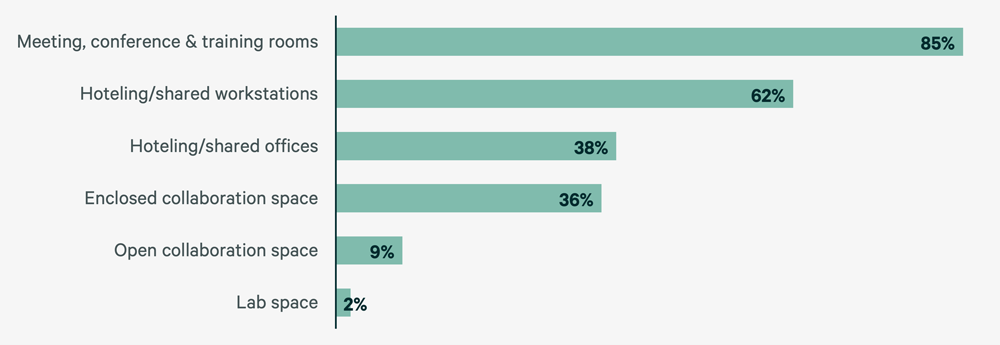
Space Reservation Management
Space reservations systems, traditionally used to book meeting space, are increasingly used by real estate teams to manage shared or hoteling workspace. Of the 88% who use a space reservation system, 85% use the system to book meeting space and 62% to book workspace.
Once seen as a solution for social distancing and employee shift-scheduling during the pandemic, workspace-booking system use slowed in 2023, as many workers returned to the office and found ample available workspaces. We expect use of the systems to increase throughout 2024, as organizations rebalance and reconfigure underutilized office space to support new hybrid work patterns. Change management and communication planning will be instrumental to the successful deployment of these tools.
Figure 7: What Spaces Are Available to Reserve in the Space Reservation System?
- How user friendly is the system: does it offer an intuitive interface for both administrators and end-users?
- Can the system scale to meet the evolving needs of your organization, and does it allow customizable configurations?
- How well does the system integrate with existing tools and systems like calendars, email and space management software?
- What analytics and reporting features are provided to track space utilization, occupancy rates and reservation trends? Do the system’s definitions align with those used in your organization?
- Does the system address compliance with privacy regulations, and what security measures are in place to protect sensitive data?
Employee Experience Applications
Employee experience applications should make navigating the physical and virtual work environments easier by providing employees a single, self-service platform for engaging with workplace amenities and services such as space reservations, wayfinding and facility requests. While these apps have gained traction over the last five years, challenges with data integration and poor change management have hindered widespread adoption. Implementation will grow throughout 2024, as organizations look for ways to attract employees to the office through connection to their peers and teams and an elevated workplace experience.
Pro Tip: When exploring employee experience applications, start by outlining the employee journey. Documenting any friction employees feel when transitioning between physical and virtual work environments will help identify specific use cases for the application to address. These use cases can help quantify the value, impact and ROI of the application to develop a strong business case.
Best Practices for Developing a Workplace Technology Toolkit
Building a workplace technology toolkit is straightforward but not easy. It starts with a deep understanding of operational readiness, as well as current and future needs. Once these are clearly understood and documented, an organization can plan a practical approach to building an effective technology stack. The following steps provide best practices organizations should consider along the way.
Start With a Diagnostic to Assess Operational Readiness
A workplace technology diagnostic provides an objective assessment of an organization’s current maturity across workplace processes and technologies. This evaluation helps identify strengths, weaknesses, gaps and potential risks to develop and prioritize future technology investments, integration opportunities, training initiatives and process improvements. Maturity is scored on a five-point scale ranging from least mature (reactive) to most mature (predictive).
- Level 1: Ad hoc tools or processes
- Level 2: Systems are not connected; processes may be defined but are not implemented.
- Level 3: Systems are partially integrated; processes are deployed.
- Level 4: Systems are fully integrated; process’ performance can be measured.
- Level 5: Systems are fully integrated and automated; processes are in continuous improvement.
Figure 8: Maturity Scale

Process Maturity
Top three characteristics of high process maturity:
- Clearly defined and documented processes
- Leverage existing technology to automate time-consuming and manual processes
- Clear definition of roles, responsibilities, data standards and governance
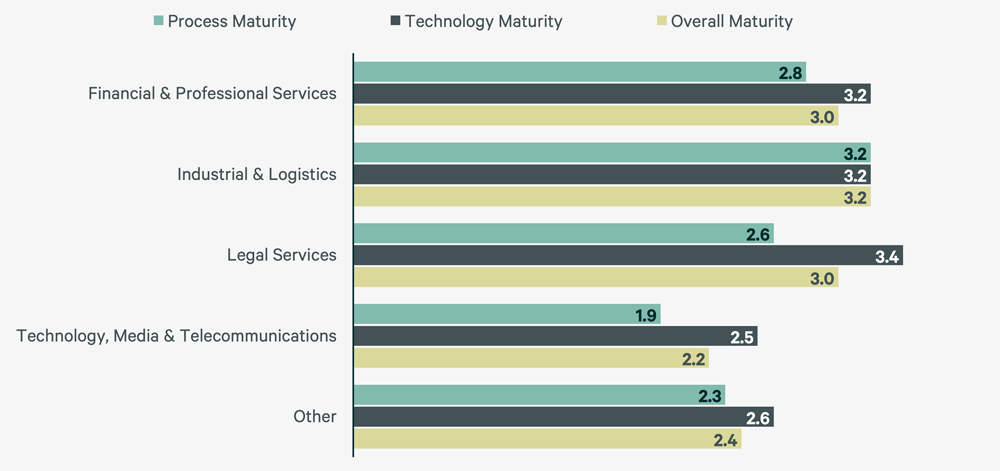
Average process maturity of CBRE Workplace & Occupancy Management clients is 2.6/5.0.
Technology Maturity
Top three common characteristics for high technology maturity:
- Globally consistent and well-implemented workplace technology
- Seamless system integrations
- Workflows aligned with business processes
Average technology maturity of CBRE Workplace & Occupancy Management clients is 3.0/5.0.
Pro Tip: Conduct annual workplace technology diagnostics that track changes in maturity year-over-year. This creates a culture of continuous improvement, reallocates resources as needed and mitigates operational risks stemming from people, process and technology changes that occur over time.
Figure 9: Average Technology & Process Maturity
Develop a Technology Roadmap
Strategically planning, implementing and managing technology initiatives requires organizations to develop an actionable workplace technology roadmap that considers both process and technology maturity. This approach is crucial for aligning technological advancements with business goals and budgets.
The top 10 reasons for creating a technology roadmap include:
- Alignment with Business Goals: A technology roadmap helps align technology initiatives with the overall business goals and objectives. It ensures that technology investments contribute to the success of the company.
- Strategic Planning: A roadmap enables strategic planningby providing a clear vision of how workplace technology may evolve over time. This helps prioritize and sequence technology projects based on strategic importance.
- Resource Allocation: A roadmap assists in the effective allocation of resources including budget, time and personnel.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying potential risks helps minimize disruptions and ensures smooth technology transitions.
- Technology Integrations: A roadmap facilitates the integration of new technologies with existing systems and processes. This ensures that the introduction of new technologies is seamless and does not create silos within the organization.
- Adaption to Change: Technology is constantly evolving and a roadmap helps adapt to technological changes allowing for flexibility in incorporating emerging technologies and adjusting the strategy in response to industry shifts.
- Stakeholder Communication: A technology roadmap serves as a communication tool for internal and external stakeholders; provides transparency about the organization’s technology strategy, which fosters understanding and support.
- User Adoption and Training: One of the most crucial steps for ensuring that employees are adequately prepared for changes in technology and maximize the benefits of new tools and systems.
- Cost Management: Outlining the costs associated with each technology initiative allows effective management of budgets, prevents cost overruns and ensures financial resources are allocated wisely.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that have a well-defined technology roadmap are better positioned to gain a competitive advantage. They can leverage technology to innovate, streamline processes and respond more effectively to market demands.
Developing a workplace technology roadmap is a strategic imperative for organizations wanting to harness the power of technology to drive business success. It provides a structured approach to technology planning, implementation and ongoing management.

Establish a Data Governance Program
Establishing a data governance program as part of an overall workplace technology strategy is an essential part of the tool kit for any organization. Many companies today even have their own Data Governance departments.
A well-defined and established data governance program is crucial for the following reasons:
- Data Accuracy and Consistency: A data governance program ensures that the space related is accurate, consistent across applications and reliable, this is vital for making informed decisions about space allocations, utilization, occupancy, and planning.
- Efficient Decision Making: Having a well-defined data governance program ensures that decision-makers have access to high-quality, up-to-date data. This facilitates more efficient and effective decision making.
- Collaboration and Communication: A standardized approach to data governance ensures that different departments within an organization share a common understanding of space related data.
- Cost Savings: Accurate and consistent data enables organizations to identify opportunities for cost savings. This could include space optimization, reducing underutilized space and implementing more efficient layouts.
- Adaptability to Change: A robust data governance program ensures that data can be easily adapted and updated to reflect organizational changes and contribute to overall success and efficiency.

The following graphic shows the CBRE propriety data governance framework, which is based on three lifecycle stages—Gather, Store, Deliver—and further grouped into process categories, covering the end-to-end data lifecycle.
The Gather-Store-Deliver framework is also used for prioritization and planning. The priorities and needs of an organization will determine which components should be addressed and delivered over time.
Figure 10: Gather-Store-Deliver Data Governance Framework

Integrating a data governance program into the creation of a workplace technology toolkit is essential for ensuring data integrity, compliance, security and overall effectiveness of technology initiatives.
Through clear definition of roles and responsibilities and consistent data-management practices and standards, company leaders can make informed, accurate, data-driven and actionable decisions.
Conclusion
Organizations must adapt their workplace technology strategies to prioritize workplace experience, embrace evolving metrics and build comprehensive toolkits.
This transformation involves not only selecting the right technologies but also emphasizing the importance of aligning technology strategies with business objectives, assessing operational readiness, developing strategic roadmaps and implementing robust data governance programs for informed decision making.
Building an effective workplace technology toolkit starts with a diagnostic assessment for operational readiness and a technology roadmap aligned with business goals, resource allocation and risk mitigation. Lastly, the establishment of a data governance program is essential for ensuring accuracy, efficiency and adaptability to change.

Organizations must adapt their workplace technology strategies to prioritize workplace experience, embrace evolving metrics and build comprehensive toolkits.
Related Services
- Consulting
Portfolio Technology
Unlock superior portfolio and asset performance with cutting-edge technologies and strategic insights, enhancing your property investment decisions...
Leverage occupancy data to empower, anticipate and unlock opportunities within your portfolio.
- Transform Business Outcomes
Consulting
Gain comprehensive guidance on insightful, executable real estate strategies for both investors and occupiers.


