Adaptive Spaces
Effective Spaces
Part 4 of Our 2024-2025 CBRE Global Workplace & Occupancy Insights Series
March 26, 2025 5 Minute Read

Subscribe for More of This Content
Introduction
Workplaces have undergone a significant transformation over the past four years, driven by technology, business process advancements and the shifting needs of employees. Hybrid work is disrupting long-standing office metrics and key performance indicators and redefining how organizations allocate and measure space. In this article, we examine the characteristics of effective office space, including today’s important considerations:
- Office-space composition: What is the ideal amount of individual vs collaboration space, density, size and amenities?
- Workplace design: How has design evolved to accommodate new ways of working, and does the perception of office usage match the reality?
- Employee experience: How can office spaces incorporate employee personas to attract and retain talent?
- Portfolio optimization: How much space does an office need to support utilization targets?
- Co-working: How important is flexibility for occupiers?
Space Composition
Recalibrating Priorities: Individual vs. Shared Space
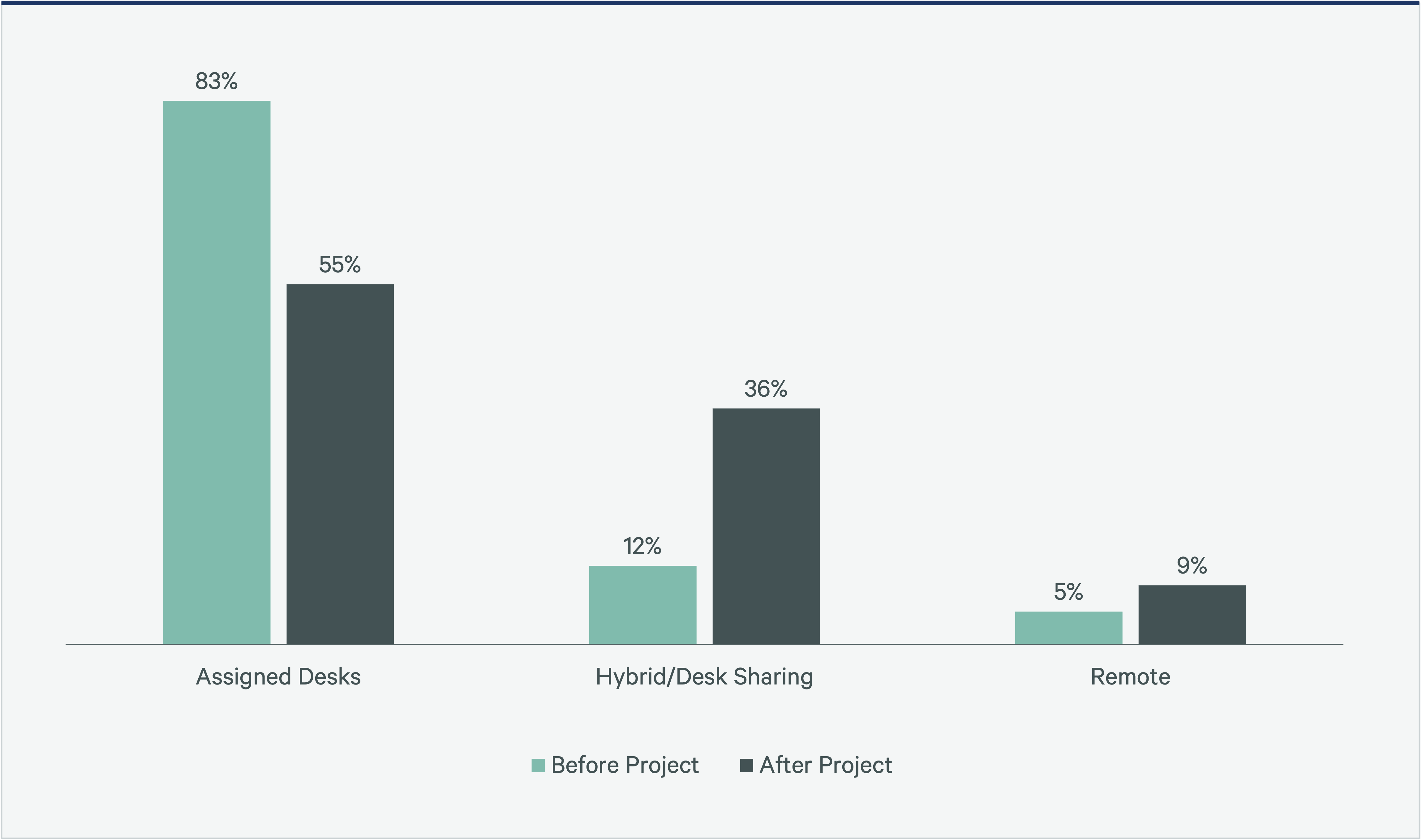
The era of 100% assigned desks in office environments has waned. According to CBRE Workplace Project Benchmarking, the percentage of companies opting for assigned seating has declined from 83% to 55%. In contrast, hybrid and desk-sharing models are gaining acceptance, increasing from 12% to 36%, reflecting a growing preference for flexibility and activity-based work environments. This shift is also reflected in the growing number of companies with unallocated hoteling and visitor seats, which grew from 5% to 9%, indicating a gradual but significant move toward this trend.
Figure 1: Seat Allocations for CBRE Workplace Projects
Target Desk-Sharing Ratios Increasing
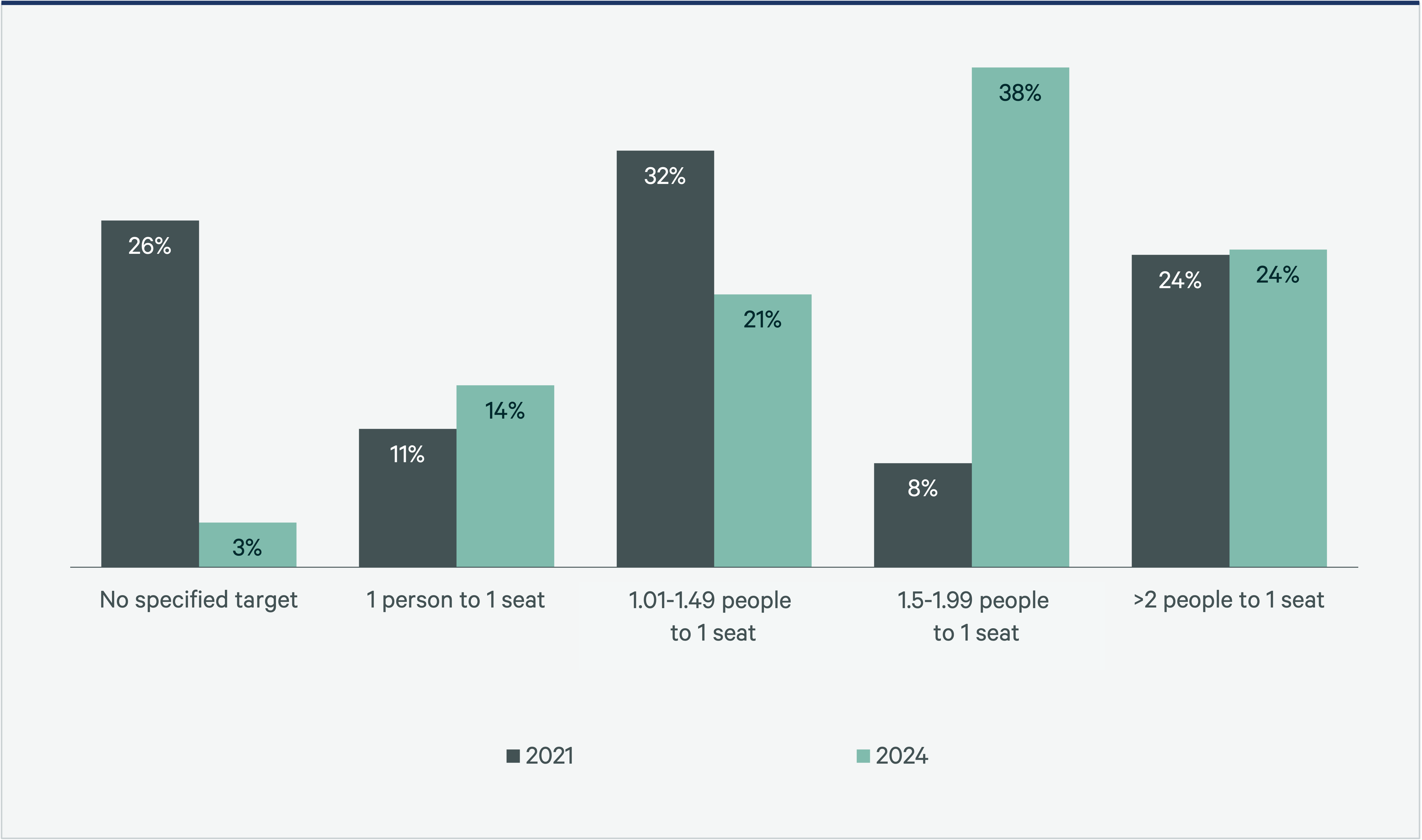
This shift is not just about space utilization; it’s a fundamental recalibration of how we work. As we have untethered from the office, the employee-to-seat ratio has risen sharply since 2021. For the first time, we are seeing 62% of organizations with a target sharing ratio at or above 1.5 employees per desk. In fact, compared with 2023, last year saw a 93% increase in target sharing ratios at greater than 2:1. Conversely, though only 14% of organizations still allocate one employee per desk, 2024 marks the first increase in four years, with the 1:1 ratio rising in popularity by 10 percentage points from 2023.
However, space allocation can be quite nuanced, and differences in organizational processes and teammate functions may lead to variations in ideal desk-sharing metrics. For example, 10% of Financial and Professional Services (FPS) companies assign one desk per employee, while 90% allocate from 1.01 to two or more employees per desk. In contrast, 43% of Technology, Media and Telecommunications (TMT) companies assign one desk per employee, while 57% allocate from 1.01 to two or more employees per desk.
Figure 2: Global Target Sharing Ratios, 2024 vs. 2021
The employee-to-seat ratio has risen sharply since 2021.
Density Is Tightening with Space Recalibration
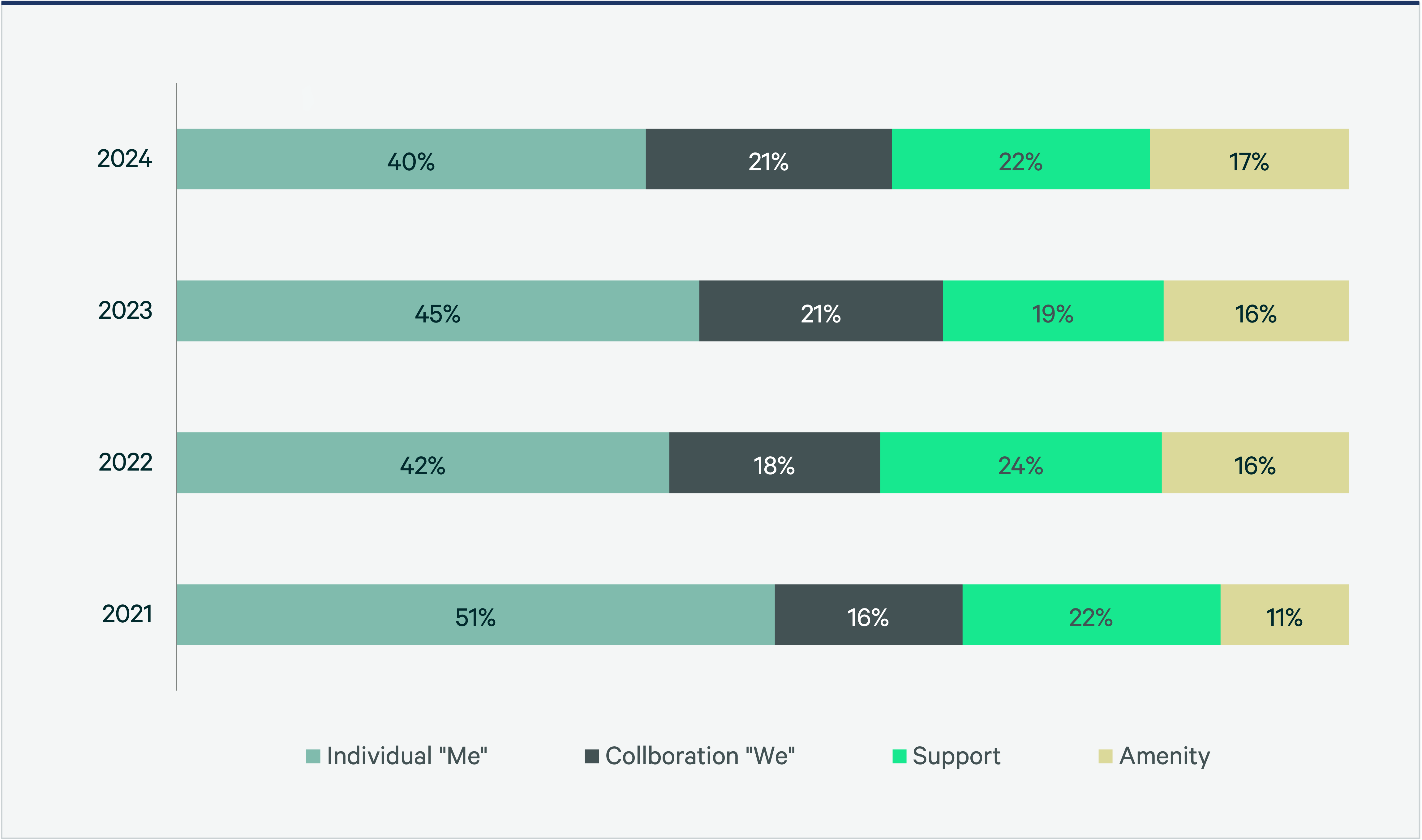
As we move toward more desk sharing, density has also tightened. CBRE Workplace saw average space allocation per employee increase from 292 to 205 rentable sq. ft. per employee, making companies 27% more efficient. However, even with fewer desks, the average rentable sq. ft. per seat slightly increased from 229 to 239.
This efficiency comes alongside a recalibration of space types to reflect a more dynamic mix of office functions, with individual spaces decreasing from 51% in 2021 to 40% by 2024. This 21% decline highlights a growing trend toward collaborative environments, as companies recognize the importance of teamwork in driving innovation, productivity and culture.
The need for collaborative space continues to evolve as workplaces move to accommodate teamwork. However, this is the first time since 2021 that we have not witnessed growth in this area. Shared space climbed from 16% in 2021 to 21% in 2023 and 2024, which indicates that companies are embracing the new balance between personal and shared space.
Individual Office Size Stabilizing
As the need for individual offices diminishes, the average size has stabilized at 100-149 sq. ft. (9-13.9 sq. m.), which represents 64% of sizes surveyed and remains the most common size in corporate portfolios. This standard has been stable over the past four years, affirming its role as the backbone of modern workspace design. Larger private offices, 224 sq. ft. (20.9 sq. m.) declined sharply in popularity from 16% to just 4%, indicating a significant realignment in space utilization and leadership preferences. Large private offices primarily served individuals but could accommodate 2-3 person discussions, and their decline underscores the increasing importance of flexible, small meeting areas for spontaneous collaboration available to a wider audience.
Workstation sizes have also seen a trend. The 35-49 sq. ft. (3.3-4.6 sq. m.) workstation, which became the standard in 2022, now constitutes 64% of workspaces, making it the most common size. This highlights the importance of personal space as well as optimizing space for efficiency and collaboration in modern work environments.
Amenities Increase in Importance
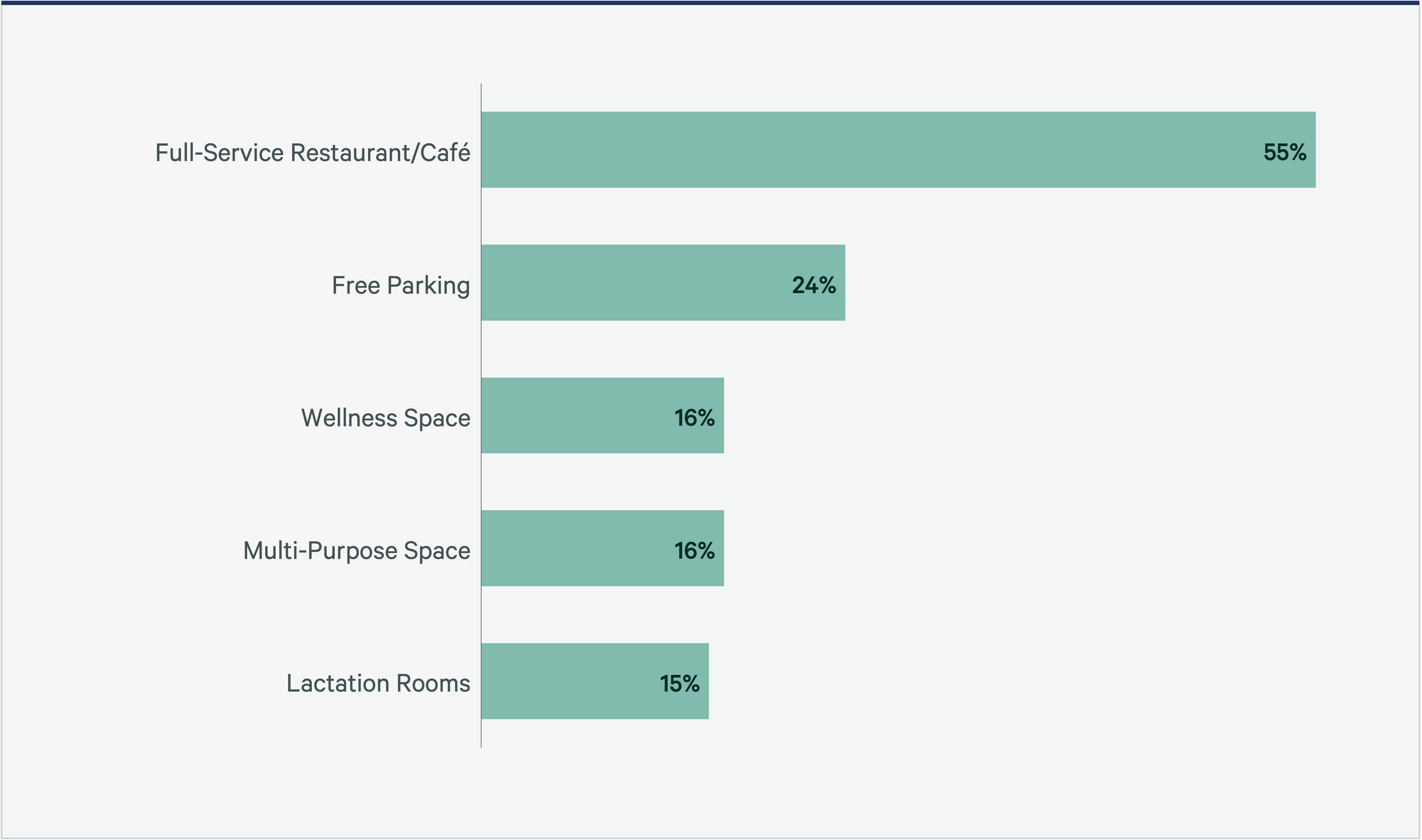
The office has begun a renaissance, fueled by a surge in employee engagement, networking and socialization. We are witnessing the emergence of vibrant, modern workspaces. Dated and sterile work environments continue to be replaced with services that transform the workspace into an experience—a curated tapestry of social hubs like restaurants and cafes that seamlessly connect to outdoor spaces, game rooms that spark creativity and flexible multipurpose areas designed for collaboration.
These aren’t just cosmetic upgrades. They represent a fundamental shift in how we perceive work and community—for example, town hall spaces with bleachers for dynamic gatherings and health-focused retreats that include quiet rooms, library-like zones and lactation facilities. While the overall increase in amenity space allocation remains modest—up a mere 6 percentage points from 11% in 2021 to 17% in 2024—this shift toward experiential spaces supports attraction and retention of an increasingly hybrid workforce.
Figure 3: Top Five Workplace Amenities
Dated and sterile work environments continue to be replaced with services that transform the workspace into an experience.
Hybrid work increased our reliance on electronic documents, accelerating paperless initiatives and stabilizing the need for support spaces (which often included storage, copy/print areas, etc.) which account for 22% of physical workplace footprints in 2024.
As organizations recognize that engaging environments are essential to attracting and retaining top talent, we anticipate a wave of innovation in office design. The future is clear. To thrive in an increasingly hybrid workforce, creating compelling, enjoyable spaces is not just an option; it’s a necessity. The office is no longer just a place to work; it’s becoming a destination for connection and culture-building.
The Evolving Workplace: Bridging the Gap Between Perception and Reality
The office, as we know it, is undergoing a seismic shift, driven by technological advancements, changing workforce demographics and evolving employee expectations. Yet, 2024 insights reveal a striking disconnect between how organizations perceive their workplace strategies and the actual state of their office spaces.
Many organizations believe their offices are primarily focus-based, but real-world data tells a different story.
The Misalignment in Workplace Design Concepts
Many organizations believe their offices are primarily focus-based, but real-world data tells a different story. There is a greater prevalence of activity-based and collaboration-based designs. This discrepancy underscores the need for a deeper understanding of workplace strategies and their true impact on employee productivity and well-being.
Figure 4: Workplace Planning Concepts
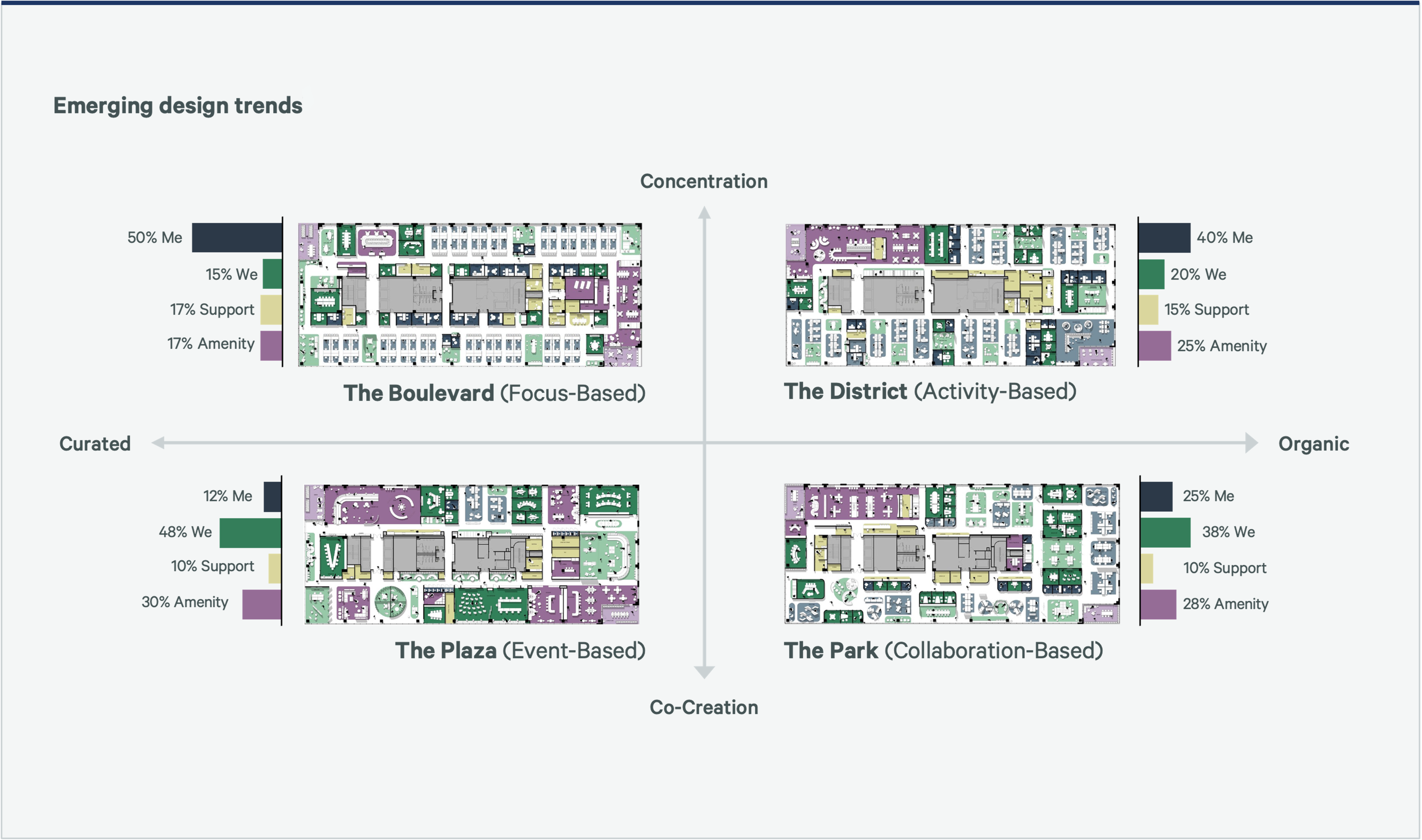
The Evolution of Workplace Design
- 2021: A Focus on Individual Work: 2021 saw a strong emphasis on focus-based design, which catered to individual work needs in the immediate aftermath of the pandemic. At the time, remote work was prevalent, and there was a need for quiet, private spaces to concentrate and be productive.
- 2022: Embracing Collaboration: In 2022, the focus shifted toward activity-based design, recognizing the importance of collaboration and flexibility. This change reflects the gradual return of employees to office spaces and the realization that teamwork and face-to-face interactions are crucial for innovation and problem-solving.
- 2023: A Balanced Approach: By 2023, organizations aimed to strike a balance between focus-based and activity-based designs. This balanced approach reflected the entrenchment of hybrid work models, where both individual focus and collaborative efforts are equally valued and necessary for a productive work environment.
These trends highlight how workplace design evolves in response to broader societal changes, technological advancements and shifting employee expectations.
Figure 5: Workplace Planning Trends
Despite this shift toward activity-based and collaboration-based designs, a significant portion of respondents (71%) still perceive their offices as focus-based. This perception gap highlights the importance of aligning workplace strategies with employee needs and organizational goals. Individual work preferences play a significant role. Employees who prefer quiet, individual work might still perceive the office as focus-based, regardless of the available collaborative spaces.
The Future of Work: A Hybrid Model
The future of work is undoubtedly hybrid, blending remote and in-office work. To accommodate this shift, organizations must rethink their workplace strategies. Key trends shaping the future of workplace design include:
- The Rise of the Experiential Workplace: Offices are becoming more than just functional spaces. They are immersive experiences, incorporating elements like biophilic design, art installations and sensory experiences to create inspiring and engaging environments.
- The Power of Technology: Smart buildings, powered by IoT and AI, are revolutionizing the way we work. From automated lighting and climate control to personalized workspaces and virtual reality collaboration tools, technology is transforming the workplace into a seamless, interconnected ecosystem.
- The Human-Centric Office: The focus is shifting from physical space to human experience. By prioritizing employee well-being, organizations can create healthier, happier and more productive workforces. Ergonomic furniture, noise-reduction strategies and flexible work arrangements are all essential components of the human-centric office.
- The Collaborative Commons: Highly functional, collaborative spaces are becoming increasingly important as teams become more distributed and diverse. These spaces should be designed to foster creativity, innovation and social interaction.
A Call to Action: Reimagining a New Era
To thrive in this new era, organizations must:
- Embrace Change: Adapt to new work patterns with new spaces. Stay open to fresh ideas and experiment with various workplace configurations, even if it means starting with temporary pilot projects.
- Invest in Technology: Employees want a better experience at work, which primarily means toiling in front of screens. Leverage technology to enhance productivity, collaboration and employee experience.
- Champion Employee Well-being: Address Gallup’s 2024 State of the Workplace finding that 66% of employees reported not thriving at work. Develop comprehensive wellness programs that support physical, mental and emotional health. Incorporate biophilic design, mindfulness spaces and flexible work arrangements to create a nurturing environment.
- Foster a Culture of Innovation: After a long pandemic, employers are now mastering basic needs and paving the way for creativity to flourish. Encourage creativity and collaboration by designing spaces that inspire new ideas and innovative thinking.

By embracing these forward-thinking strategies, organizations can create workplaces that are not only functional but also inspiring, engaging and sustainable. The future of work is not just about adapting to change—it's about leading it.
Understanding Personas to Improve Employee Experience
Since the pandemic, individual ways of working have changed, and distinct personas have emerged that reflect different workspace needs. Some employees have grown accustomed to working at home, accommodating their needs and preferences for everything from the physical desk and chair to the technology set-up required to do their best work. As more employees are required to return to the office, organizations are working harder to support individuals’ in-office work. For instance, employees often desire access to enclosed spaces for confidential conversations or readily available tech-enabled meeting rooms for mixed-presence collaboration. In other words, people want task-specific spaces.
In addition to the quality of space that matters, the provision of seats needs to directly correlate to team working patterns. Understanding these different personas can help improve the employee experience and create a more effective workplace that is purposefully designed to accommodate a variety of workstyles. Notably, workstyle and persona have become the top factors influencing workstation assignment, with 56% of companies now prioritizing these criteria, up from 47% in 2023.
Figure 6: What criteria determines if an employee is assigned a workstation?
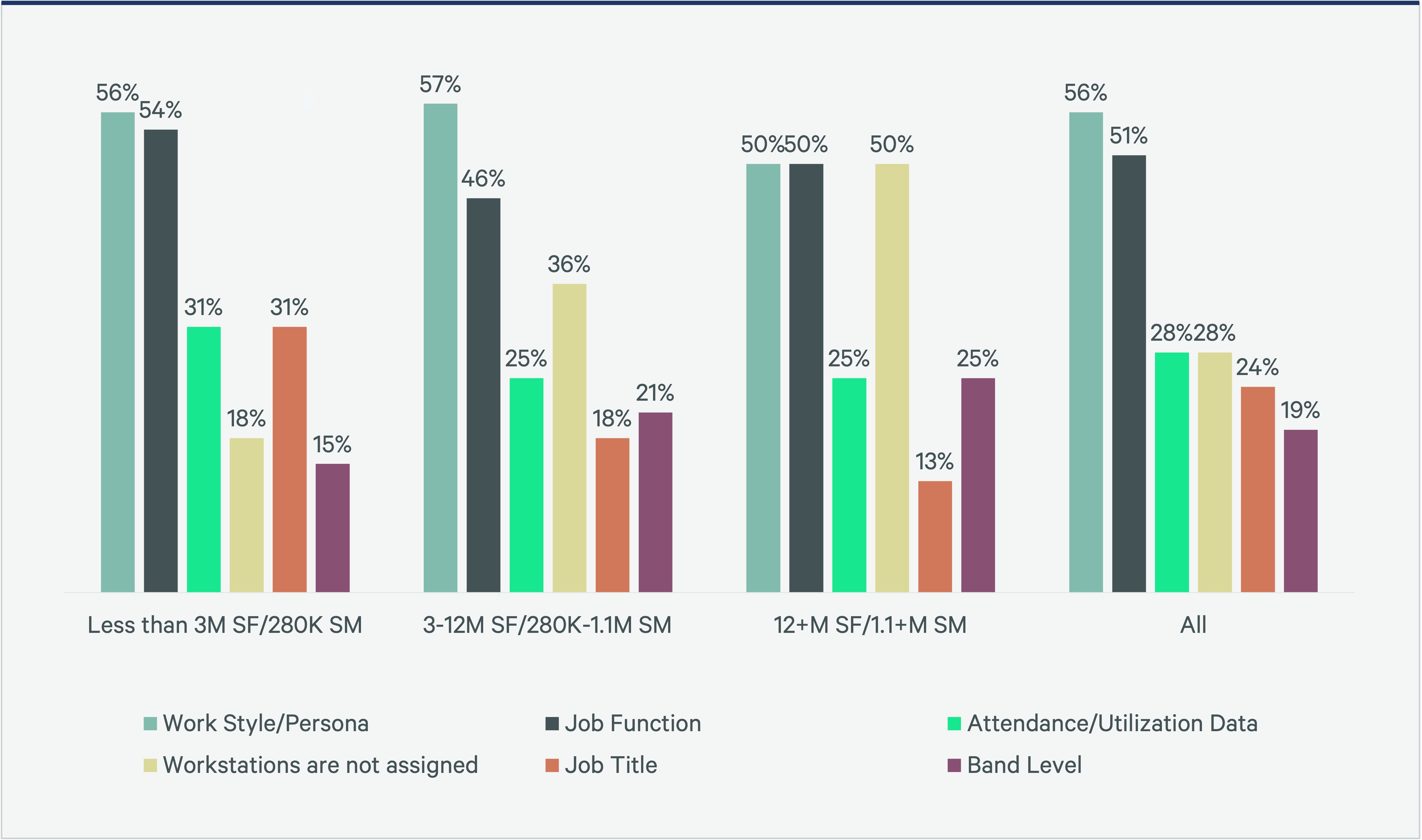
Job function, while important, no longer dictates employees' workstyles. A more holistic understanding of workstyle composition can fully align office space to new ways of working. Workstyle personas look different from company to company. Analyzing these patterns, we have defined five contrasting sets of workplace needs and preferences.
- Individual vs. Collaborative Work
- Local vs. Multiregional Stakeholders
- Scheduled vs. Unscheduled Interactions
- Dynamic vs. Quiet Environments
- Universal vs. Specific Needs
A combination of these factors, often segmented by team functions, can inform detailed recommendations for space mix and design. As individual offices decline, utilization of collaboration spaces continues to rise, especially for enclosed spaces like walled conference rooms. According to XY Sense Workplace Utilization Index from Q2 2024, enclosed meeting room utilization (58%) is more than double the utilization of open areas (23%), indicating that users still prefer to meet in enclosed areas, most likely for visual and audio privacy. This is also true for private focus areas. Utilization of private focus areas runs 21% higher than for open workstations, reflecting a growing need for quiet zones in the office.
Aligning spaces to workstyle personas ensures a better functional fit for employees and creates a more dynamic environment that enhances employee experience, collaboration and culture-building.
Portfolio Optimization Now Balances Expansion/Contraction Strategies
For the past four years portfolio optimization has been the most common corporate real estate goal at 81%, followed closely by driving cost savings at 76% and increasing office utilization at 72%. Accordingly, on average, 69% of office portfolios greater than 3 million sq. ft. have undergone significant reductions since that time, as companies began implementing plans for a hybrid future. The primary strategies that have been used to achieve these goals have been reducing underutilized space, renovating existing space, or accommodating growth within the existing portfolio.
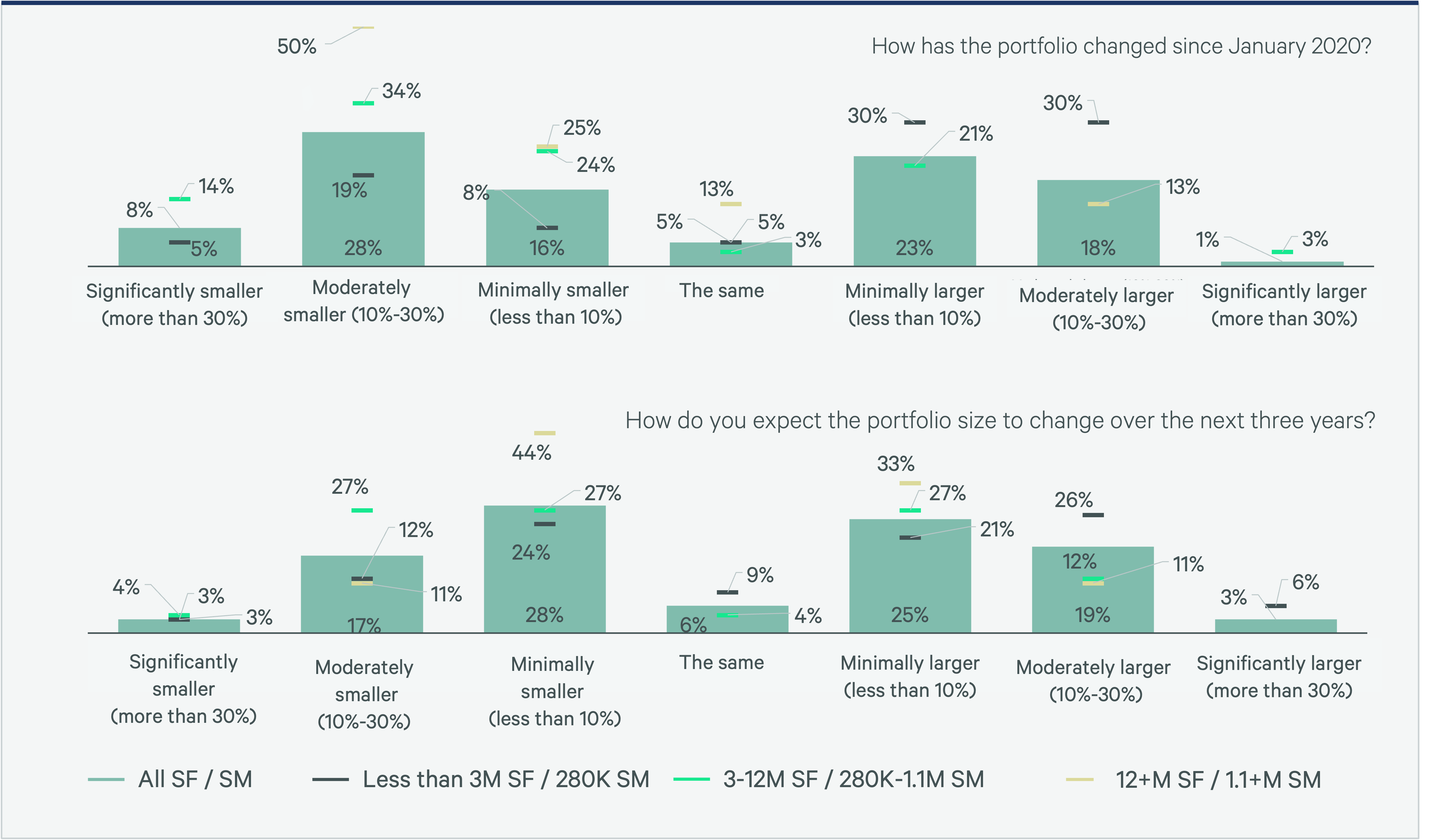
In 2024 portfolio reductions stabilized, with 52% of companies reporting that their portfolios have shrunk, down from 62% in 2023. The data further supports this shift, with 44% of respondents indicating that they are expecting expansion overall in the next three years, while 48% still expect contraction—a more even distribution than exhibited in the past four years. Additionally, more occupiers are beginning to include where they should strategically expand in their portfolio strategies, due in part to market opportunities and the renewed focus on in-person attendance.
Figure 7: Portfolio Changes 2020-2027
Companies Using Co-Working Space Strategically
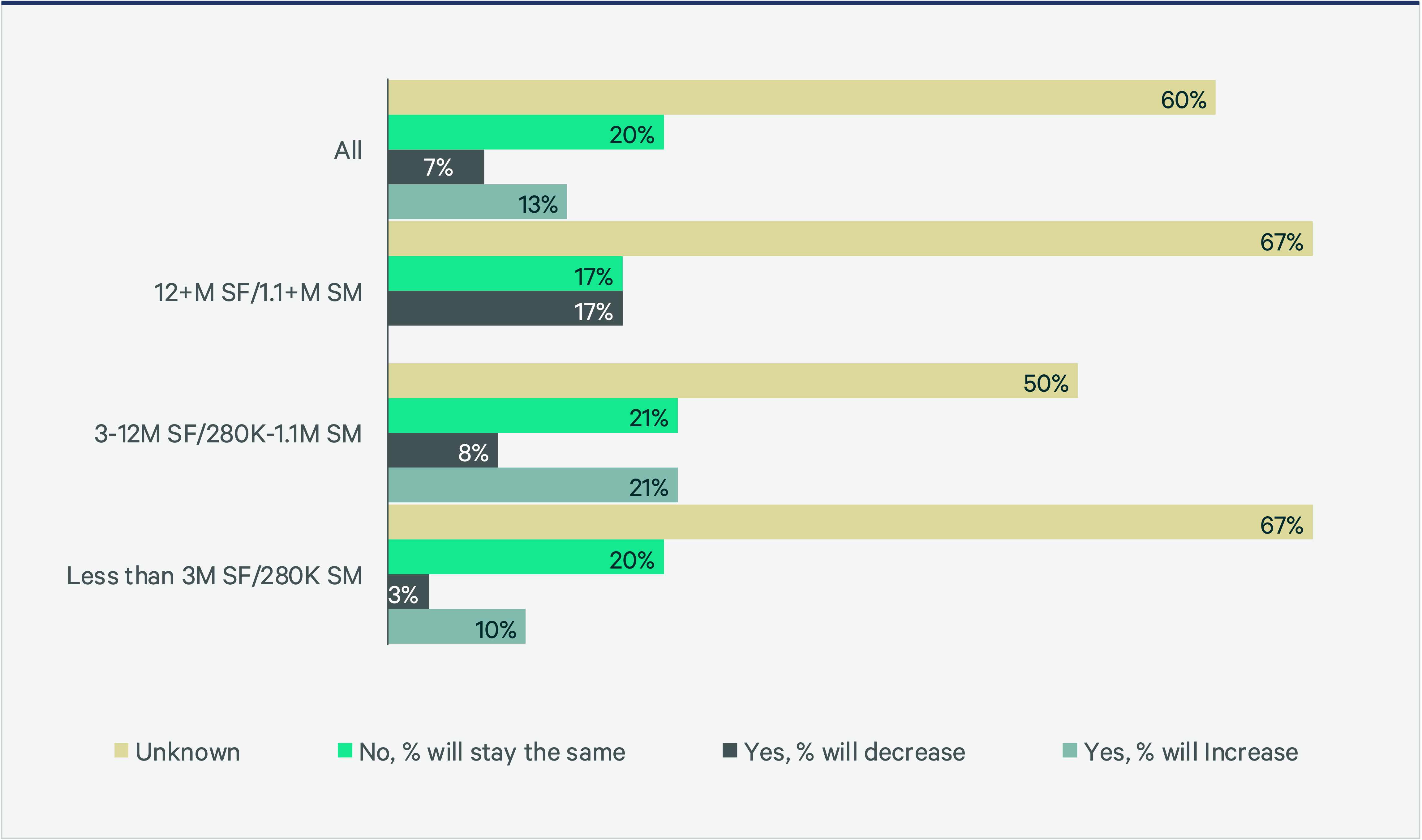
Flex office space has become an essential tool for companies aiming to support their growth and contraction strategies, mitigate uncertainty and accommodate a distributed workforce. This trend is evident in the shift toward a more balanced approach to portfolio growth versus contraction strategies and their noticeable stabilization. In particular, medium-sized portfolios of 3-12 million sq. ft. are planning to either increase (21%) or maintain (21%) their use of flex office space, while larger portfolios of more than 12 million sq. ft. are more inclined to decrease (17%) or maintain (17%) their current use of flex office space.
Figure 8: In the future, will the % of co-working space in the portfolio change?
Globally, the most common reasons for co-working are flexible commercial terms (30%), location options (18%) and cost (18%). From an industry perspective, sectors such as Technology, Media and Telecommunications and Financial and Professional Services have the most clearly established strategies for utilizing flex office space. These industries leverage flex office space primarily for its flexible commercial terms (43% and 33%, respectively), location options (14% and 17%) and cost (14% and 33%). However, many other industries are still in the exploratory and experimental stages of adopting flex office space.
Industrial and logistics (I&L) companies account for a surprisingly significant portion of the increase. Nearly two-thirds of I&L companies will either grow their flex footprint or maintain it. They are primarily leveraging flex office space to manage headcount variability (43%) and cost (29%).
Figure 9: Common Reasons for Co-Working by Industry
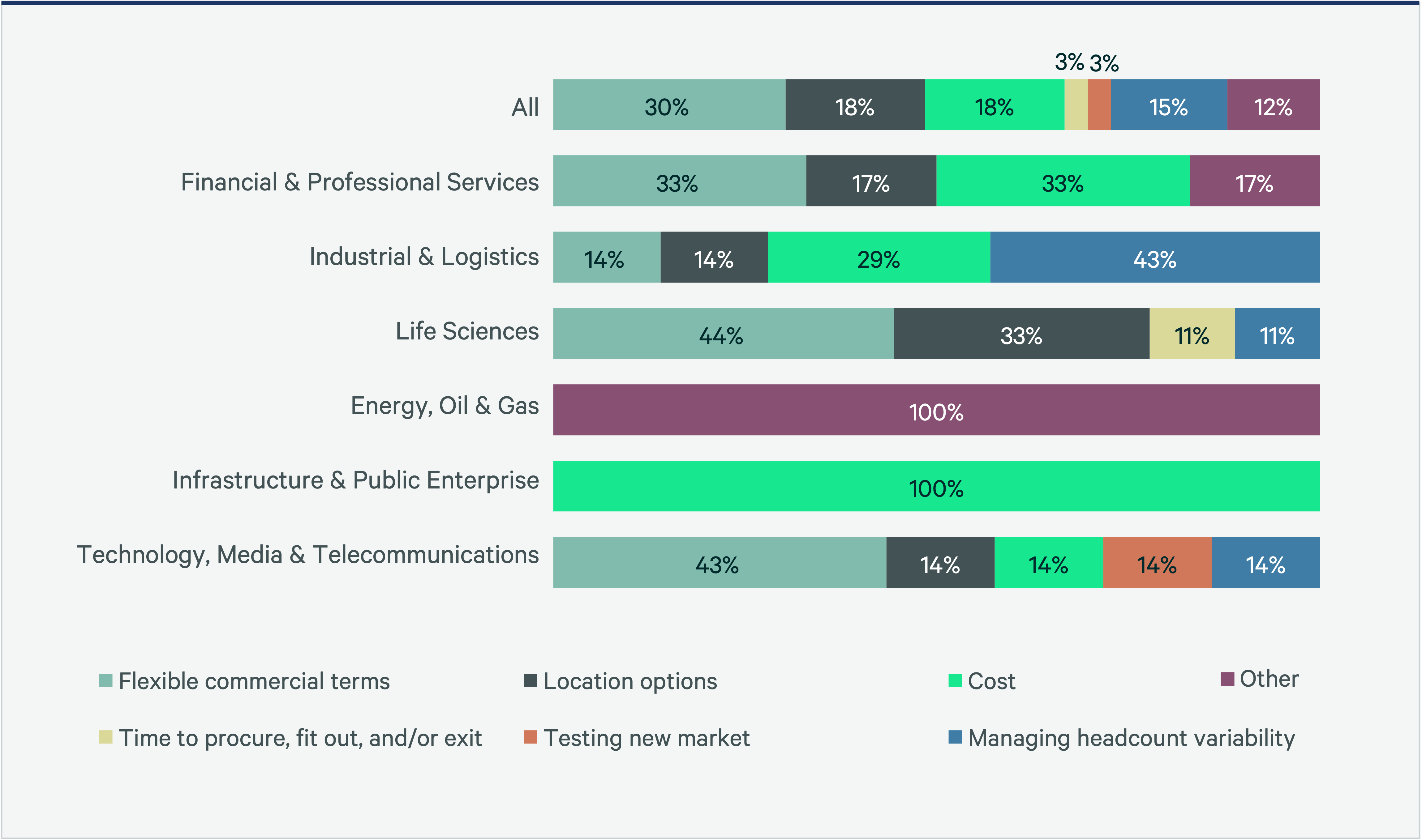
While the adoption of flex office space varies across different industries, it plays a crucial role in supporting companies' strategic objectives and operational flexibility. These trends highlight the growing importance of flex office space in the business landscape.
Conclusion
The traditional office is obsolete. The shift to hybrid work necessitates a radical redesign of workplace environments, moving away from static layouts and assigned desks toward dynamic, flexible and human-centric spaces. Companies must adapt to attract and retain talent, offering inspiring and engaging offices that foster creativity, collaboration and well-being; the rise of the experiential workplace reflects this demand. These spaces incorporate biophilic design, technology and art to enhance the employee experience.
However, a significant disconnect exists between organizational perceptions of workplace strategy and the reality of their office spaces. Many cling to outdated models, failing to prioritize the activity-based and collaborative environments that are crucial for a hybrid workforce. To fully realize the potential of the hybrid model, organizations must embrace evolving work patterns, invest in technology, champion employee well-being and cultivate innovation. The future workplace seamlessly integrates work and life, fosters community and belonging and offers a truly exceptional employee experience.

Occupancy Optimizer
Amid the increasing volume, velocity and variety of available data, portfolio, workplace and occupancy strategists must challenge the status quo and adopt new approaches. Ultimately, effective strategists can assimilate the abundant amount of internal and external data to make well-informed real estate decisions. One innovative strategy we have implemented is leveraging machine learning to automate the process of restacking a building or campus based on various data inputs. CBRE's Occupancy Optimizer tool is a component of a larger technology suite of tools known as Portfolio Optimizer. The Occupancy Module serves as an AI-supported stack plan generator, enabling strategists to streamline the stacking process, making it less manual and more automated.
Occupancy Optimizer replaces what planners do manually to create site and/or campus stacking plans. It employs data science and machine learning to analyze inputs collected by our teams, which include current and projected headcount growth, actual utilization trends by business unit/department and adjacency requirements or constraints. This allows it to automatically restack a building, optimizing for efficiency, space requirements and/or or adjacency considerations, saving approximately 20 hours per generated plan.
About the Series
CBRE’s 2024-2025 Global Workplace & Occupancy Insights is a five-part series that explores trends across major office occupiers, providing valuable insights for organizations seeking to align their workplaces with business needs and cultural objectives. Part 1, “Companies prefer metrics that measure effectiveness, rather than efficiency,” explored how organizations are increasingly prioritizing workplace experience as a crucial factor in real estate success. In parts 2 and 3, we explored how effective workplaces require strategic hybrid programs, which have increased in adoption by 30% over the past four years. Part 2, “Effective Hybrid Programs: Policies and Common Characteristics,” outlined the factors that contribute to the effectiveness of various hybrid program models. In Part 3, "Effective Hybrid Programs: The Experience,” we explored the tactical tools needed to transform office policies into reality. In this article, Part 4, we explore the characteristics of effective office spaces.

Office Occupancy Management Benchmarks
Leverage our Tableau dashboard to enhance occupancy decision-making. Customize filters to focus on your specific sector and region.
Contacts
Carole Hunter
Managing Director | Americas Consulting

Susan Wasmund
Executive Managing Director, Americas Consulting | Global Occupancy Management

Related Insights
-
Article | Evolving Workforces
Effective Hybrid Programs: Policies & Common Characteristics
January 22, 2025

Hybrid work models have become the dominant workplace strategy. Implementing and measuring these models has evolved.
-
Article | Adaptive Spaces
Companies Now Prefer Metrics That Measure Effectiveness, Rather Than Efficiency
October 29, 2024

The first in our 2024-2025 CBRE Global Workplace & Occupancy Insights series offers insights on redefining metrics to gauge the success of workplace strategies.
Related Services
Leverage occupancy data to empower, anticipate and unlock opportunities within your portfolio.
- Plan, Lease & Occupy
Workplace Consulting
Build resilience, attract and retain talent, and foster connection and collaboration in your workplace.
- Transform Business Outcomes
Consulting
Gain comprehensive guidance on insightful, executable real estate strategies for both investors and occupiers.
- Plan, Lease & Occupy
Organizational Change & Transformation
Enabling organizations to achieve outcomes, improve performance and create change-ready cultures.







